
Computed Tomography (CT) uses a strong dose of X-rays to capture internal images of the human body from multiple angles. Advanced computer technology is then used to combine multiple sets of extremely thin cross-sectional images to form a clear three-dimensional image to show the body. The condition of internal organs. Depending on individual patient conditions, medical staff may need to take, inject, or inject a contrast agent through an enema before undergoing a computer scan to enhance the clarity of the examination site.
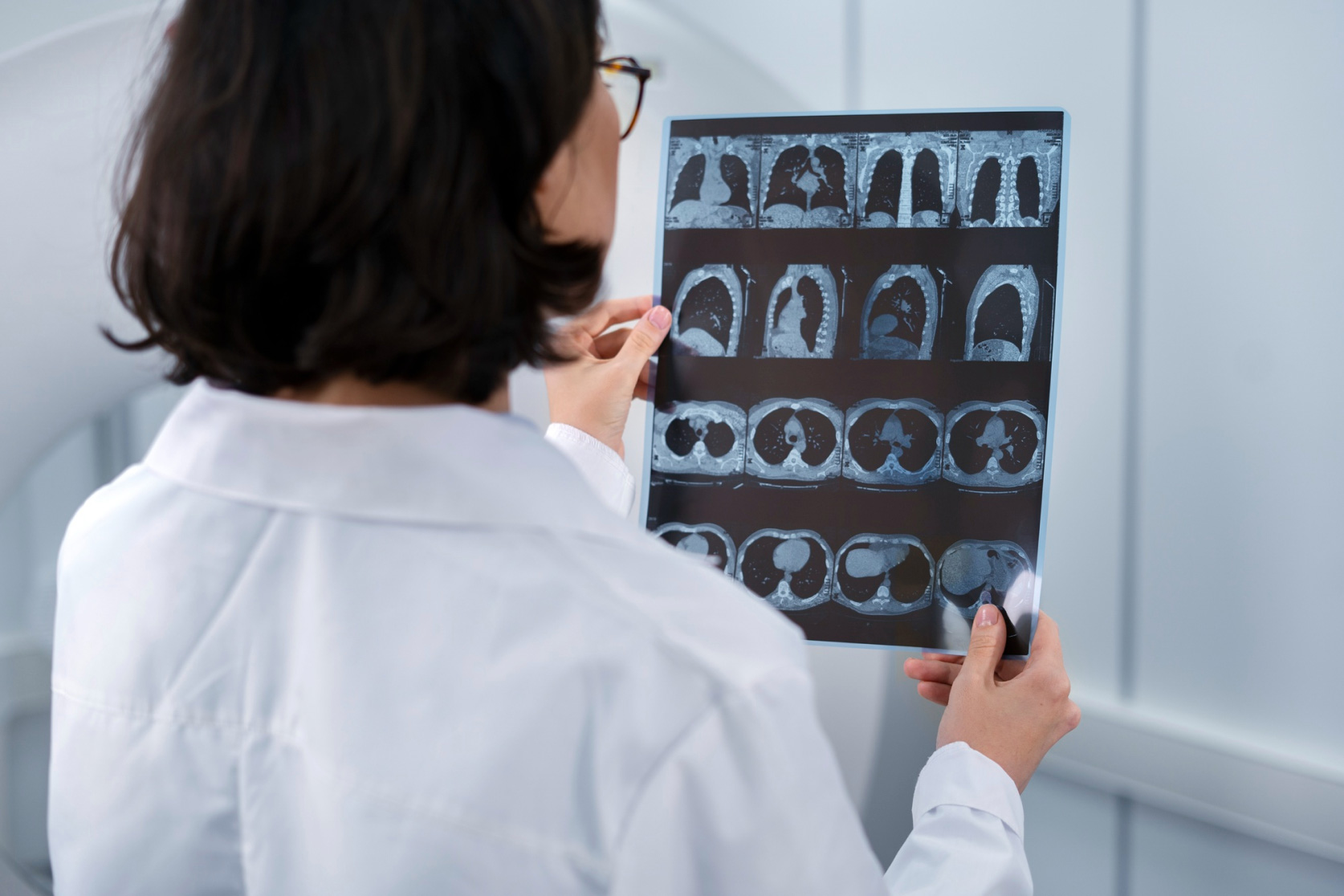
Computer scans are widely used and are generally used in the head, neck, chest, abdomen and pelvis to provide detailed images of multiple tissues, such as blood vessels, bones and soft tissues. For example, it can be used to detect and check whether there are cancer lesions on the body or perform cancer staging, check whether there are structural lesions in coronary arteries or other blood vessels, cerebrovascular lesions related to stroke, diagnose infectious diseases such as tuberculosis, and guide needle extraction. Biopsy and other issues. Computer scanning can also help doctors formulate and plan surgical plans.Safety instructions
